Management of Reusable Medical Devices and Integrated Operating Room Scheduling Problem: A Column Generation Approach with Machine Learning
Reducing operational costs and utilizing resources more efficiently in hospitals has become a growing challenge in the healthcare sector. Effective surgical scheduling plays a critical role in enhancing service quality in hospitals and ensuring operational efficiency. However, operational factors such as the sterilization and maintenance of reusable medical devices (RMDs) can cause disruptions in surgical scheduling and reduce the efficiency of operating room resources.
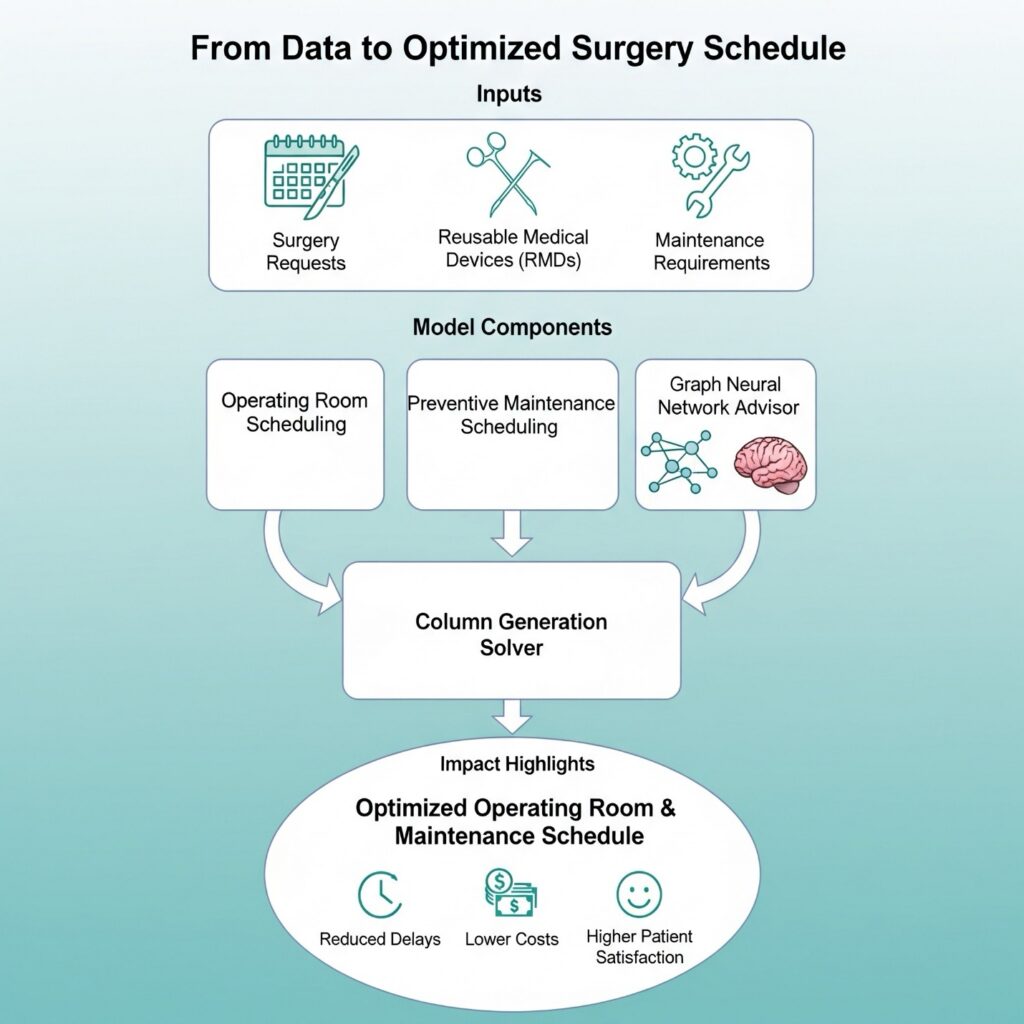
This project aims to develop an innovative model that integrates surgical scheduling with the sterilization and preventive maintenance planning of RMDs to optimize hospital resource utilization. The preventive maintenance scheduling problem requires tracking the usage count of each RMD and sending it for maintenance once a predefined threshold is exceeded, necessitating the individual tracking of each RMD in the system.
The developed model will be solved using a column generation algorithm, and its efficiency will be enhanced through the application of Graph Neural Networks (GNN). GNN will analyze operating room data to generate the closest optimal scheduling plan, enabling a more dynamic and realistic optimization of surgical scheduling.
The most significant contribution of this project to the healthcare sector is improving the efficient use of operating room resources and preventing surgical delays. Specifically, integrating surgical scheduling with RMD processes will allow for more effective management of hospital operational processes. Additionally, the developed model and methodology can be applied to various hospitals and healthcare systems, contributing to overall healthcare service efficiency.
In the future, adapting this model to different healthcare systems is expected to reduce hospital operational costs and enhance patient satisfaction. Furthermore, the artificial intelligence-based column generation method developed in this project has the potential to be utilized in other fields that involve similar logistics and resource management challenges.